
Dementia can be heartbreaking for patients and their families. As memory fades, expressing basic needs becomes harder. This is where speech therapy for dementia patients comes in. Speech therapy focuses on helping adults with dementia preserve their communication skills and maintain quality of life. While dementia cannot be cured, working with a speech-language pathologist offers practical support. At Precision Speech Therapy, our clinicians provide personalized care that addresses both cognitive and communication needs of older adults.
Table of Contents
Why Speech Therapy for Dementia Patients Matters
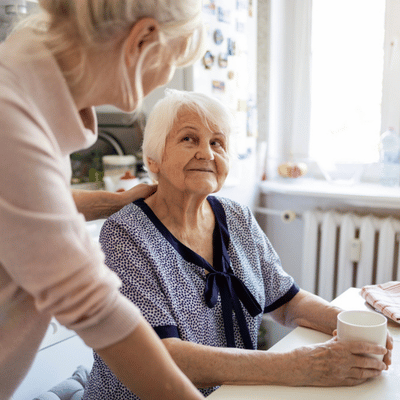

More than 55 million people worldwide live with dementia. This number is expected to nearly double every 20 years, according to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA). Individuals with dementia now represent one of the largest patient groups seen by speech-language pathologists.
Speech therapy for dementia patients is considered “maintenance” therapy. The aim is not to reverse dementia but to maintain skills for as long as possible. Experienced clinicians note that the primary goals are to:
- Keep the individual functioning at their best
- Reduce the caregiver’s burden
- Maintain the person’s sense of self
ASHA states that the overarching goal is to maintain quality of life for as long as possible. SLPs help people remain independent by working on attention, memory, and problem solving. By participating in adult speech therapy for dementia, individuals can experience less frustration and stay socially connected.
Key Goals of Speech and Language Therapy
SLPs tailor speech and language therapy for dementia patients to each person’s needs. Below are the key objectives and their benefits:
Preserving Communication Abilities
A primary goal is to help the person maintain speaking, understanding language, and finding words. Speech therapy for dementia patients uses exercises that can sharpen remaining language abilities or introduce alternative ways to communicate. For example:
- Practice naming objects
- Use simple phrases to express basic needs
- Implement gestures and facial expressions
Maintaining these skills keeps the person engaged with loved ones.
Supporting Cognitive-Communication
Many people with dementia struggle with memory, attention, and problem-solving. Cognitive communication therapy for dementia patients targets these areas. SLPs provide tailored cognitive exercises to stimulate memory and thinking. This might include:
- Memory activities (recall games or sequencing tasks)
- Attention-training exercises
- Strategies to assist with understanding conversations
Research shows that combining language practice with cognitive training can improve memory, attention, and communication skills. It can even boost quality of life for patients and caregivers.
Maintaining Daily Function and Independence
Another goal of speech therapy for dementia patients is to prolong the patient’s ability to handle everyday tasks. Therapy focuses on practical communication skills needed for daily living. This includes:
- Understanding and following a routine
- Remembering important information
- Using tools like phones or medication reminders
By practicing these skills, patients may continue to perform self-care tasks longer.
Ensuring Safe Swallowing and Nutrition
In later stages, swallowing difficulties often emerge. This increases the risk of choking or pneumonia. Speech therapy for dementia patients addresses this crucial area by evaluating swallowing and recommending:
- Specific food textures
- Posture adjustments or swallowing exercises
- Mealtime routines and cues
Managing swallowing issues helps prevent complications like malnutrition or pneumonia.
Reducing Agitation and Anxiety
Communication problems can cause frustration and agitation. Regular speech therapy for dementia patients provides mental stimulation and routine, which can have a calming effect. SLPs might introduce:
- Picture boards
- Memory books with family photos
- Visual calendars
These tools not only aid interaction but also reassure and orient the person.
Educating and Training Caregivers
A crucial goal of speech and language therapy for dementia patients is supporting caregivers. SLPs teach effective communication strategies. For example:
- Speaking slowly and using yes/no questions
- Using written reminders and labels around the house
- Creating memory books or visual schedules
By reducing caregivers’ burden through education, therapy ensures strategies carry over into everyday life at home.
Techniques and Strategies Used in Therapy
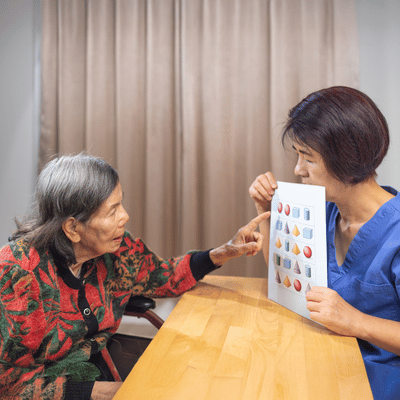

To achieve these goals, speech therapists use evidence-based techniques. These are always tailored to the individual’s stage of dementia.
Memory Aids: Therapists create memory books, visual schedules, or cue cards with important information. Tools like calendars and labeled photographs support memory day-to-day.
Communication Boards: For patients struggling to speak, picture boards or simple speech-generating devices can help. These aids allow the person to point to images for “hungry,” “pain,” or “bathroom.”
Spaced Retrieval Practice: This memory technique helps patients recall information over gradually increasing intervals of time. Research shows it helps retain important information long-term.
Montessori-Based Activities: Many SLPs incorporate hands-on tasks that align with interests and past roles. This could be sorting objects, folding towels, or arranging familiar items.
Throughout these interventions, cognitive communication therapy for dementia patients emphasizes functionality and compassion. Therapy sessions are designed to be meaningful and tailored to the person’s life.
Frequently Asked Questions
When should I start speech therapy for a loved one with dementia?
It’s never too early to involve a speech therapist. In early stages, speech therapy for dementia patients focuses on teaching memory techniques while the person can still learn new strategies.
How long does speech therapy for dementia patients last?
Therapy is ongoing and adjusts as needs change. The focus is on maintaining skills for as long as possible rather than a fixed endpoint.
Will insurance cover adult speech therapy for dementia?
Many insurance plans cover adult speech therapy for dementia when medically necessary. Check with your provider for specific coverage details.
Can speech therapy help with swallowing problems?
Yes. Speech therapists are trained to evaluate and treat swallowing difficulties, which are common in later stages of dementia.
What can I do at home to support therapy?
Use the strategies your SLP teaches, such as memory books, visual cues, and simplified communication. Consistency is key to maintaining skills.
Does speech therapy work for all types of dementia?
Yes. Speech therapy for dementia patients can benefit individuals with Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and other types.
Living Life to the Fullest
Dementia may steal memories, but it does not have to silence your loved one. Through speech therapy for dementia patients, those living with dementia can continue to engage in meaningful ways. They can express their needs and feel heard. With the right support and strategies, a person with dementia can still share moments of joy and connection every day.
Ready to help your loved one communicate better? Contact Precision Speech Therapy today to learn how our compassionate team can support you through this journey. We’re here to help your family stay connected.





